In this section we’ll explore a wide range of AI solutions by looking at practical examples.
In recent years, AI has appeared in the headlines and sparked debate from many different angles. However, it’s useful to remember that most of the stories that make it into the news are unusual and don’t involve everyday solutions, where AI is almost imperceptible. Developers in the field have sometimes reiterated that when AI becomes part of software, it’s no longer even called AI – it’s just software.
The following examples illustrate some practical AI solutions. We have divided the examples into three categories: natural language processing, machine vision, and numerical solutions.
A) Natural language processing (NLP)
Written or spoken language is at the core of NLP artificial intelligence solutions. Examples include:
Chatbots
You’ve probably already come across chatbots on corporate websites. They are able to answer customer questions or ask questions (with varying degrees of success). Chatbots are among the most common AI solutions that are directly visible to users.
A chatbot could be seen as smart because it knows how to chat with people. However, a chatbot doesn't actually understand the questions it’s answering, even though it might be able to provide a suitable answer. Also, not all chatbots are based on AI. Instead, some have pre-programmed chat paths, making it difficult for users to know which type of chatbot they are interacting with.
Language translation and speech recognition
AI solutions that translate language have rapidly become widespread. For example, Google Translate can immediately translate spoken or written text into the language of your choice.
Speech recognition is one of the key aspects of NLP. In some online stores, it allows customers to make purchases – for example, they can say “one nonfat milk” and the AI solution will interpret the content of their speech and add the product to a shopping cart.
NLP also makes it possible to check the grammar of a passage of text, and commercial applications are available for this purpose.
Interpretation of customer feedback
Companies are very interested in customer feedback, and a useful AI solution for this purpose is sentiment analysis. Sentiment analysis reveals the tone of customer feedback, from positive to negative.
Sentiment analysis is also suitable for audio recordings of customer service interactions. In this case, the AI solution translates the speech into text before analyzing it.
The domain of Natural language processing (NLP) has shown the most promise from Generative AI. The latest techniques of Generative AI has not only advanced the performance of traditional use cases like chatbots, language translation, interpretation of text but also spearheaded new innovative use cases e.g. generating marketing messages in different tonality or language that is personalised towards the customer, personalised sales agents to guide the customer throughout different customer journeys etc.
Sign up to solve exercises
B) Machine vision
Machine vision consists of image and video processing, and there are numerous uses for the technology. Here are a few examples of machine vision applications:
Face and object recognition
Common machine vision solutions include a mobile phone's face recognition function and automatic image tagging on social media. With these, machine vision can identify objects that are visible in images and videos such as people, animals, and objects.
The example in the figure illustrates machine vision in action.
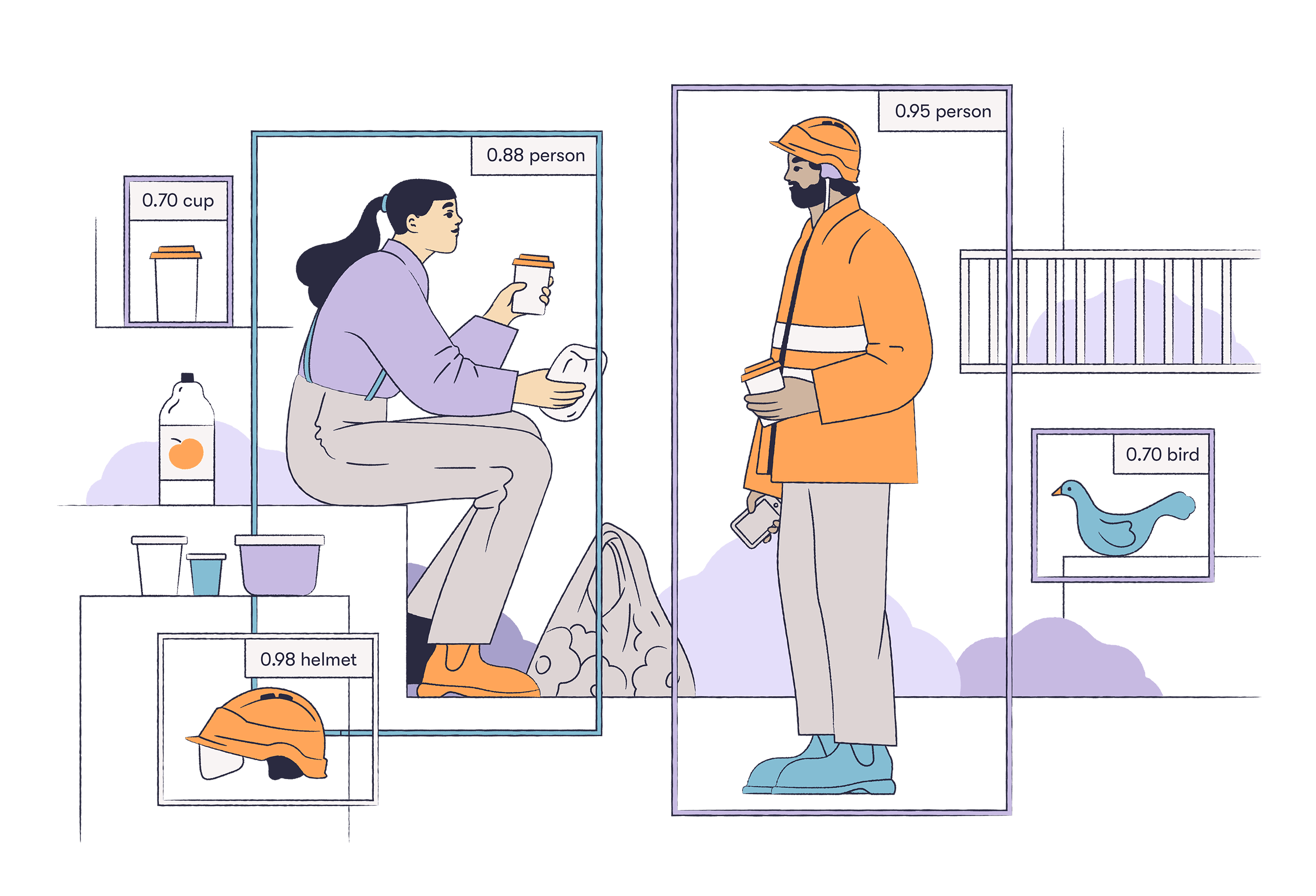

The AI solution has identified objects inside the rectangles in the image. The number (confidence) on the side of the rectangle, which uses a scale from 0 to 1, tells you how confident the AI solution is in its identification of the object.
Generating & Editing image and video content
AI can be used to generate and edit visual content. Typical examples of this are prompt based video creation (e.g. deepfake or otherwise), stylized images, or even the rejuvenation of older actors in a film. Such AI solutions are making it increasingly difficult to distinguish real content from fake content. Generating videos based on human prompts, but grounded on real-world physics and situational data could also see a lot of applications in the built environment e.g. in automation of creation of digital twins.
Quality control
One of the most common industrial uses of AI is the identification of defective products through machine vision. The object to be identified can be a wooden, metal, or paper surface, a bottle label, a weld seam, taping – really any object that provides images for AI to analyze. These solutions are popular because AI solutions never get tired and can always focus fully on the task at hand. Leveraging techniques that are foundational to advancements in Generative AI have also shown great promise in improving the performance of such conventional applications of AI in quality control. Some examples of how such techniques can help to improve the performance of conventional applications of AI are:
Data Augmentation: Generative models can create diverse and comprehensive datasets by simulating defects, enhancing the training process.
Rare Defect Simulation: Generative AI can model rare defect scenarios, ensuring that AI systems are well-prepared to identify uncommon issues.
Improved Robustness: By training on a wider range of synthetic defects, AI models become more robust and accurate in real-world applications.
Sign up to solve exercises
C) Numerical AI solutions
The previous examples relate to the processing of non-structured data like text, audio, image, or video. However, AI solutions are also able to work with structured or tabular data. These applications are often less general purpose than the solutions presented above, and as such they tend to be organization-specific. Some examples include:
Forecasting sales
Many retailers use AI to predict sales. With as many as tens of thousands of products on offer, it would be difficult for these companies to predict product order volumes without an automated system.
Automatic loan decisions
A loan decision can be obtained online almost immediately once the applicant has provided the necessary information. An AI solution uses this information to assess the applicant's creditworthiness and derive the level of risk involved in order to determine the interest rate of the loan offered.
Customer churn analysis
Telecom operators and insurance companies often use AI to perform customer churn analysis. This helps them predict which customers are likely to leave in the near future so that they can, for example, make offers to retain their loyalty.
Pricing
AI is useful for setting prices. A good example of this is the automatic pricing of used cars and homes, where AI can use background information on an item for sale to predict its probable asking price.
Customer segmentation
In customer segmentation, AI groups customers into segments based on purchasing behavior. These segments could be like “families with children” or “sports fans”.
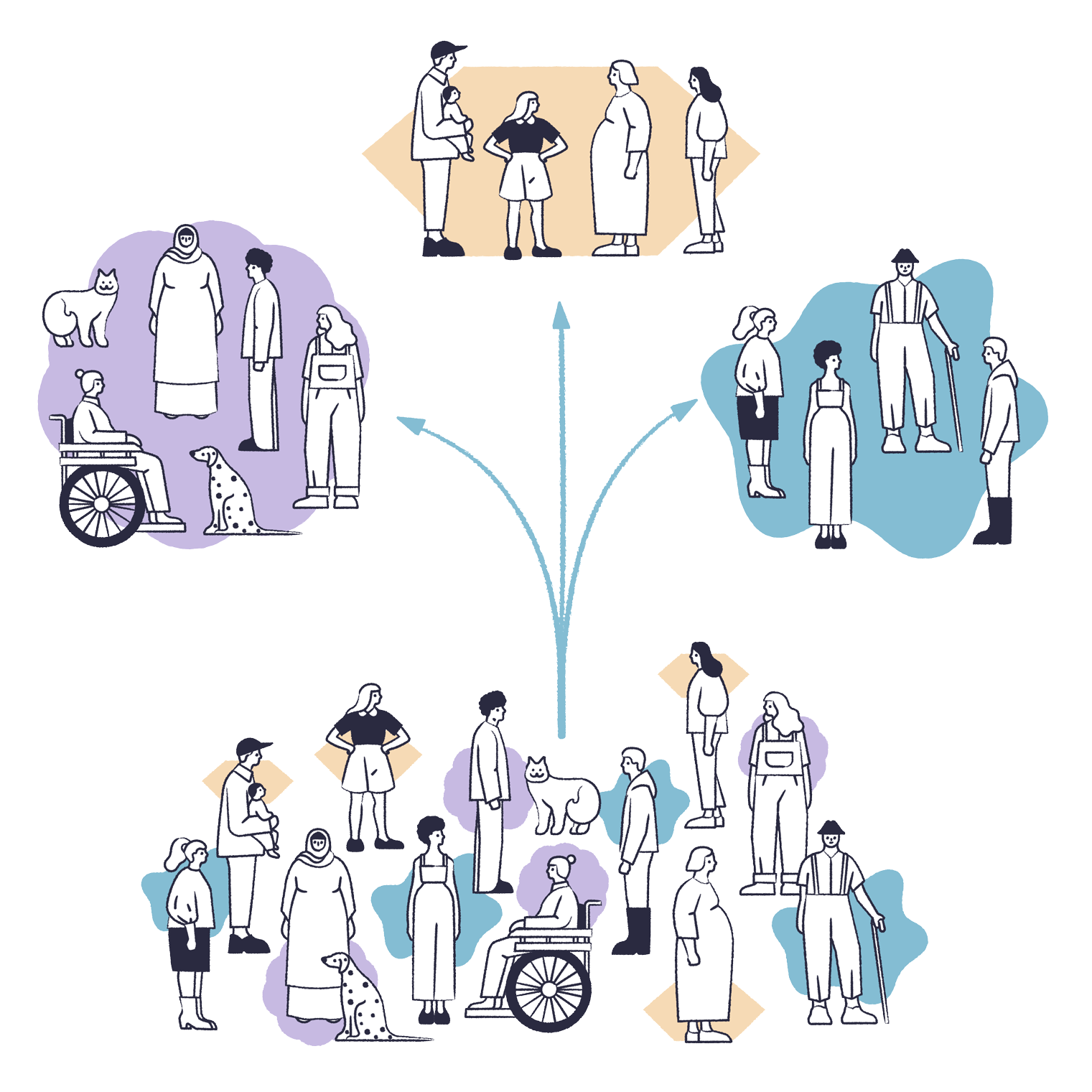

With the help of AI, we can carry out customer segmentation based on customers’ purchasing behavior. For example, the grouping with a purple background could consist of customers whose shopping carts often contain pet food.
Generative AI based tools like ChatGPT has further democratised the analysis of such tabular data. Power that was once only within the ambit of experts endowed with mathematical analysis skills, is now accessible to normal users by leveraging tools like ChatGPT to analyse data in spreadsheets. Any person with access to such generative AI tools can now analyse data, get insights & recommendations, perform scenario analysis by posing questions in normal human language.
We have seen some examples of solutions that use AI above, but what exactly is AI? We’ll look at that in more detail in the next section.

